3D Printing Technology : A Comprehensive Beginner’s Guide
Despite being around since the 1980s, 3D printing is a relatively new technology now being cultivated and utilized in various sectors. The application of 3D printing and additive manufacturing has been beneficial owing to their manifold benefits in rapid prototyping, detecting design flaws, making quick iterations, minimizing waste, and more. This blog gives a detailed overview of the 3D printing concept helpful for those interested in the technology.

What is 3D printing?
Three dimensional printing is an additive manufacturing technique in which a digital design is used for the development of a physical object. In this process, the design of an object is created with the help of CAD software and then, a 3D printer is used for developing the object by successively adding thin layers. To help you understand better, let us divide the process into three steps.
- In the first step, you need to create a 3D file with the help of 3D modeling. If not, you can also download it online and use a scanner to print the 3D file.
- The second step is where the actual process of 3D printing starts. You can first start with choosing the materials for your object you are about to print. Then, you can use 3D sculpting software for giving a definite shape to your models. The various materials you can choose for the process are resin, sand, plastic, ceramic, textile, glass, food, metal, biomaterials, lunar dust, etc. Apart from creation, you can use also these materials for finishing purposes.
- In the third step, 3D printing machines can be employed to print the desired objects. However, you cannot use or deliver it right after it is printed. Before it is ready to use or delivered, you need to give it a finishing touch by sanding, lacquering, or painting it.
Types of 3D printing technologies
Here’s a brief overview of the different types of 3D printing technologies.
-
Stereolithography (SLA)
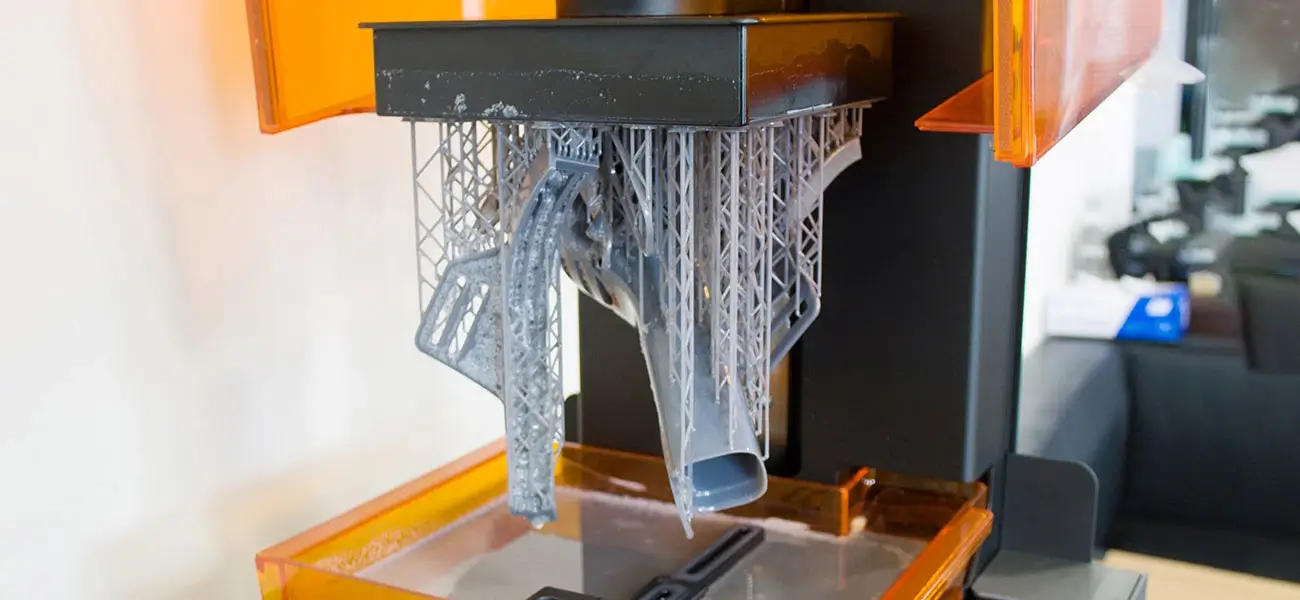
This 3D printing technology uses liquid plastic as its source and creates models and prototypes layer by layer. Liquid resin is put into a vat with a transparent bottom which is then subjected to a UV laser to form a pattern on the resin and solidify a layer of it. The structure thus solidified is dragged up by a lifting platform to allow the laser to create the desired pattern for each layer. Eventually, the 3D object is obtained.
-
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
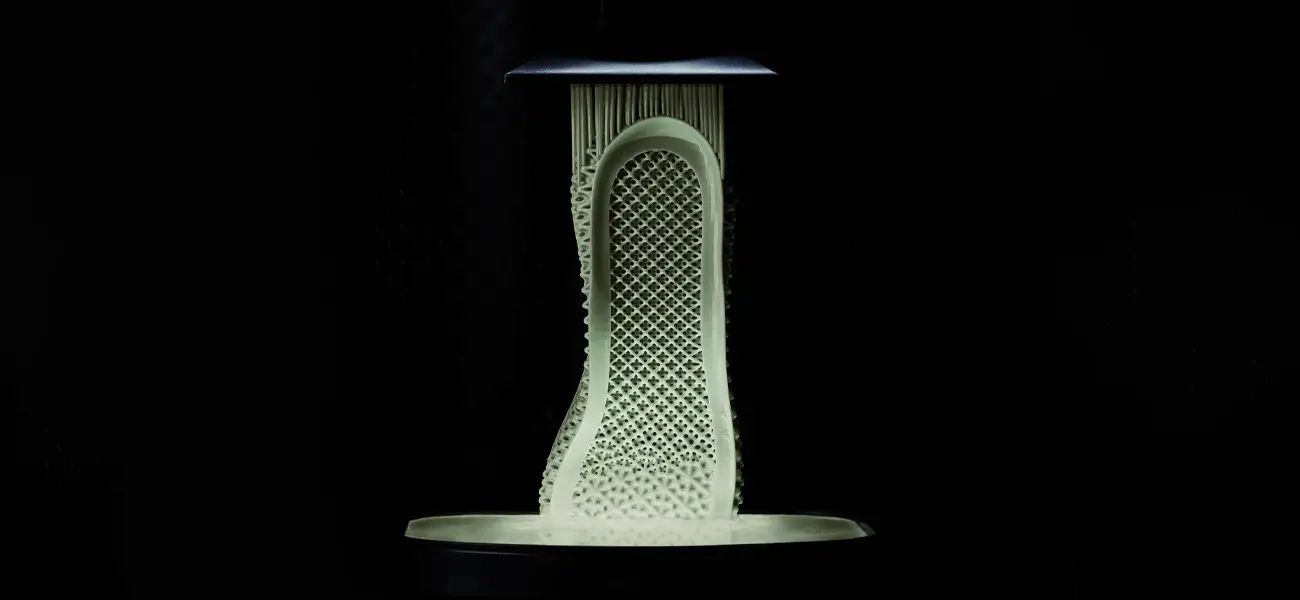

There is not much difference in the way Digital Light Processing and Stereolithography work. However, the light source that DLP uses comes from a liquid crystal display panel unlike the UV laser in stereolithography. In DLP 3D printing, micro mirrors are used to control the light incident on the object surface.
-
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
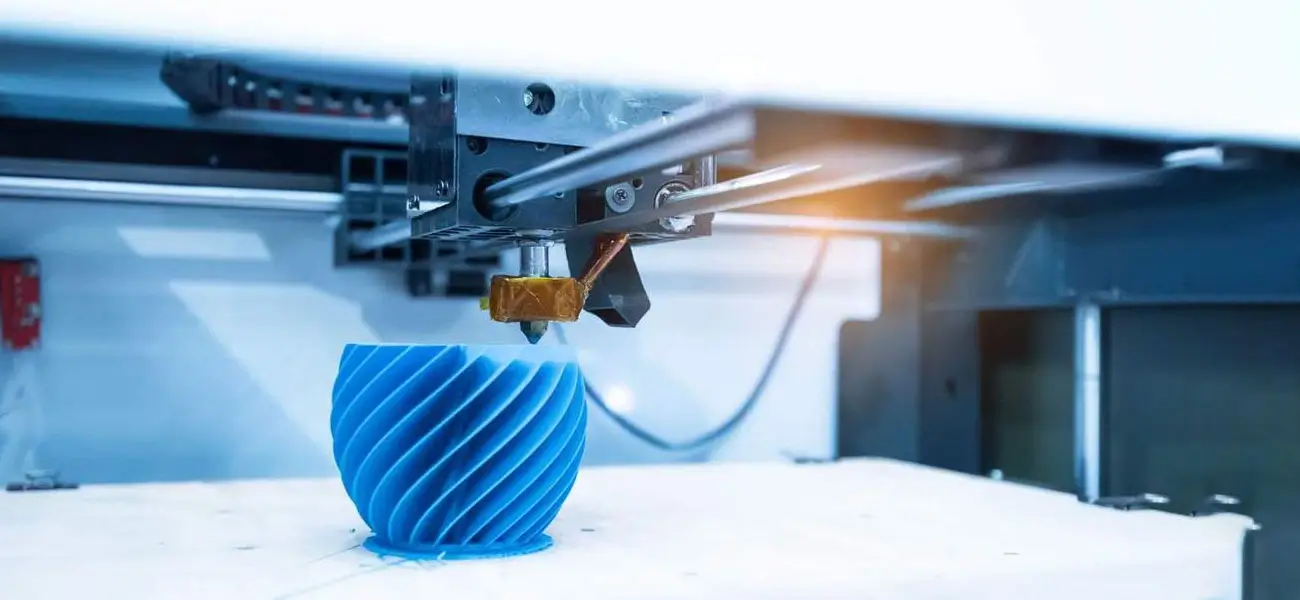

The fused deposition modeling technology involves heating a thermoplastic filament until it melts down and then extruding it layer by layer to obtain the desired structure. To create structures that are more complex, special and modified techniques may be used.
-
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
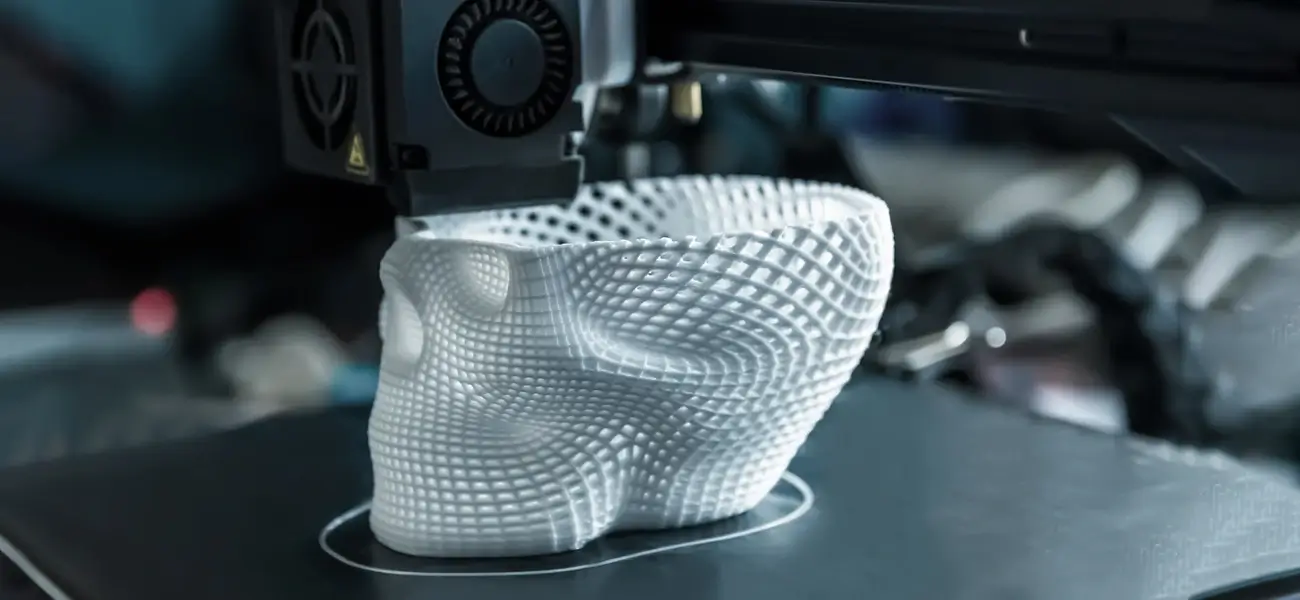

SLS does work like stereolithography in some ways, however, it places powdered material instead of liquid resin in the vat. Every layer is topped with another layer of the powdered material which is then laser sintered. A certain pattern is followed during the process to create the required object.
-
Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
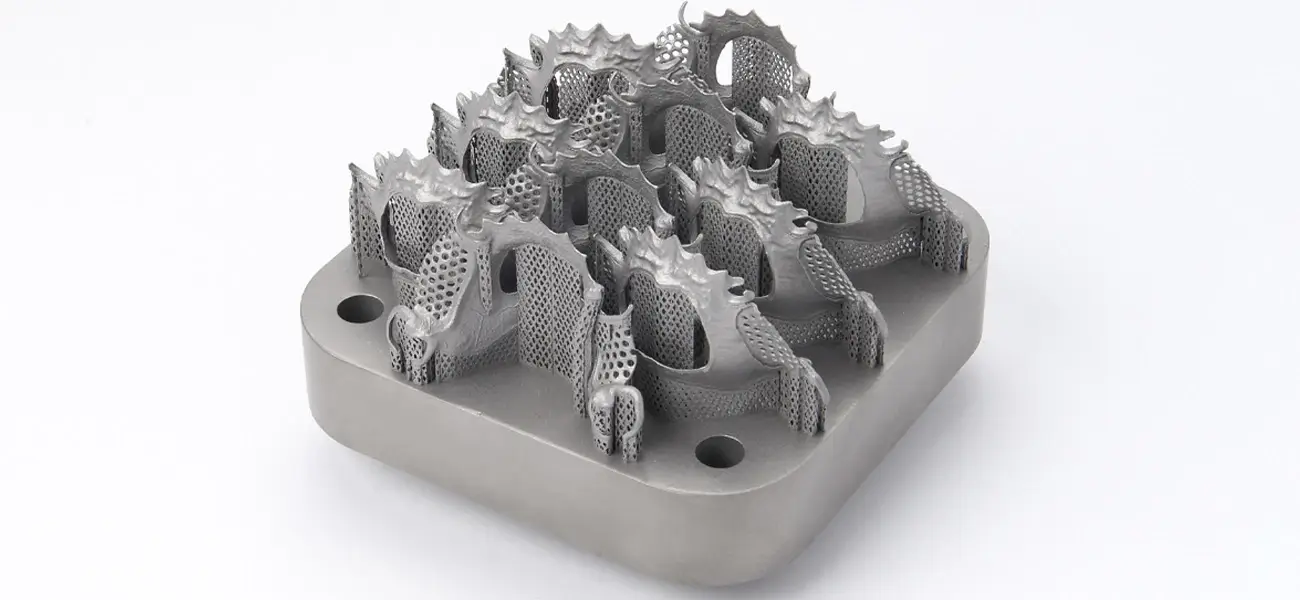

Selective Laser Melting works in a similar fashion like SLS. The only difference is that the powdered material is completely melted instead of being sintered.
3D printing applications
The uses of 3D printing are increasing with each passing day. The technology has already penetrated deep into the manufacturing and construction sectors and is most likely to reach other domains as well. However, in this article, we will be focusing only on the important ones.
-
Architecture
3D printing technology can be utilized in the production of architectural models that accurately depict the vision of the architects. Many architectural companies rely on this technology since it helps in creating detailed and high-quality models in a fast and economical manner.
-
Medical
The technology is being used for a host of applications in the medical field. It is used to create prototypes that can be used in the production of various medical and dental products. Direct manufacturing of stock items as well as patient-specific products is also possible with its help.
-
Automotive
The automotive sector mainly uses this technology for prototyping purposes. However, it can also help in taking the manufacturing process to the next level by incorporating the advantages of improved materials, which can be achieved through 3D printing technology.
-
Jewelry
The design and manufacturing of jewelry usually require a high level of expertise since it involves a lot of processes like fabrication, casting, molding, etc. However, 3D print-ready designs allow more freedom to create innovative 3D designs and cut down the lengthy traditional process to direct production.
In the early stages of 3D printing, it was only utilized for prototyping and manufacturing purposes. However, now, it has been transformed into a production technology. As the 3D printing technology is always advancing, we are most likely to witness a change in the use of materials, hardware, and processes to develop the objects and their parts. If you are planning to implement it for your projects, then go for it and enjoy the wide spectrum of capabilities it offers. However, beginners should keep in mind that they are bound to face challenges while using this technology. So, the only piece of advice we can offer is to take sufficient time to learn the skills and then utilize it for the completion of the projects. In case you do not want to go through the trouble, you can always seek help the companies specializing in 3D printing design services. Just choose the service provider depending on your budget, function, or design, and get the expected outcomes as per your needs.



